MEASURING BLOOD PRESSURE
To obtain an accurate measurement of blood pressure, it is necessary to adopt a series of procedures that include the preparation of the patient before taking blood pressure, technique used by the health worker, selection of a quiet space, and use of an accurate blood pressure monitor. Good practice includes taking measurements on both arms at the initial visit, and then continuing to use the arm with the highest measurement. At follow-up visits, two or more readings should be taken at each visit and the mean calculated.
HEARTS AND BLOOD PRESSURE MEASUREMENT
HEARTS in the Americas has identified that the issue of accuracy of blood pressure measurement is key to ensuring the advancement of the initiative as it is a crucial factor for the correct diagnosis and management of hypertension. Measuring blood pressure with non-validated equipment is a serious problem of quality of health services and a matter of patient safety. Therefore, it is working with countries on the use of correct measurement protocols, validation of automated blood pressure measuring devices, and strengthening regulatory frameworks to guarantee the exclusive use of validated devices.
Virtual Course on accurate automated blood pressure measurement (2020)
Improve timely diagnosis of hypertension and the quality of treatment in essential hypertensive patients to prevent cardiovascular complications.
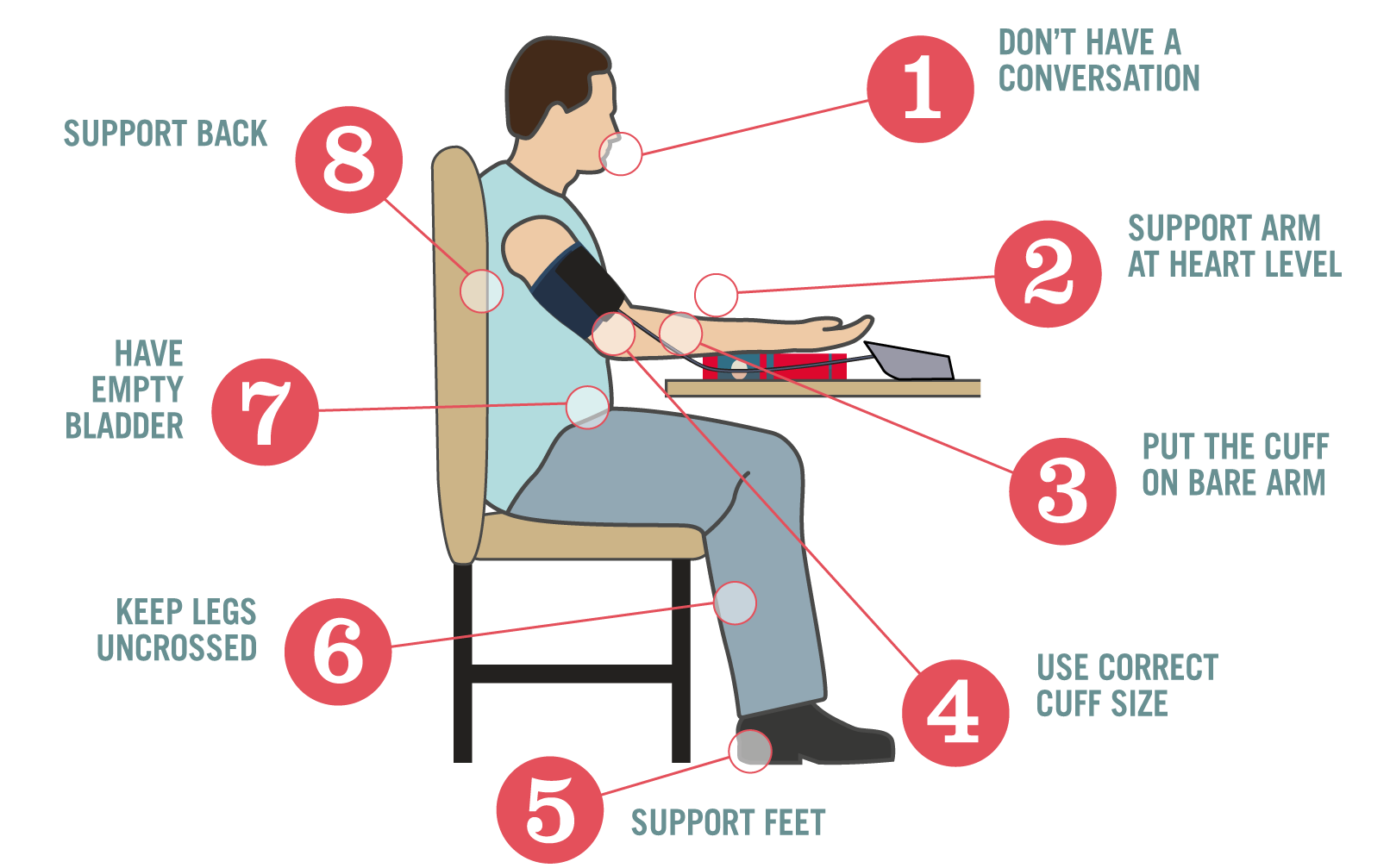
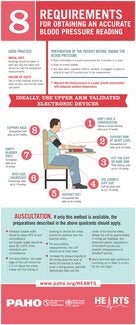
REQUIREMENTS FOR OBTAINING AN ACCURATE BLOOD PRESSURE READING
1. Use validated automated monitors or, if not available, calibrated aneroid devices.
2. Measure blood pressure in a quiet place.
3. Follow the protocol below:
— Don´t have a conversation. Talking or active listening adds up to 10 mmHg
— Support arm at heart level. Unsupported arm adds up to 10 mmHg
— Put the cuff on bare arm. Thick clothing adds up to 5-50 mmHg
— Use correct cuff size. Cuff too small adds up to 2-10 mmHg
— Support feet. Unsupported feet adds up to 6 mmHg
— Keep legs uncrossed. Crossed legs adds up to 2-8 mmHg
— Have empty bladder. Full bladder adds up to 10 mmHg
— Support back. Unsupported back adds to mmHg
Related Materials
HEARTS in the Americas: Regulatory Pathway to the Exclusive Use of Validated Blood Pressure Measuring Devices
This publication seeks to contribute to meeting these recommendations by providing a practical tool for governments to improve their national regulatory frameworks to improve accuracy of blood pressure measuring devices (BPMDs), in turn contributing to the exclusive use of accuracy validated automated BPMDs in primary health care (PHC) facilities by 2025. This publication can also guide the development of procurement mechanisms that will ensure exclusive availability of BPMDs in PHC facilities. Specifically, this publication will provide a brief background on the importance of using validated BPMDs and highlight key elements of regulations related to pre-market approvals to promote accurate BPMDs.
WHO technical specifications for automated non-invasive blood pressure measuring devices with cuff
The document presents WHO’s guidance on blood pressure measuring devices (BPMDs), and it responds to concern about the lack of accurate, good-quality devices, especially in low-and middle-income countries. The focus of the publication is on automated non-invasive BPMDs with cuff, including characteristics, regulatory requirements and standards
Technical resources relevant to the accuracy of blood pressure measurement
In this note we present a compilation of the most relevant available technical resources in the three key components of the HEARTS blood pressure measurement strategic area. The resources listed include links to scientific articles, and technical and communication materials developed by PAHO and other institutions. The purpose is to provide resources that can be useful for policy makers, health professionals, regulatory agencies, professional societies and the public.
Recommendations from the HEARTS in the Americas Workshop on Regulatory Frameworks and Procurement of Blood Pressure Measuring Devices for Use in Primary Health
The recommendations emerging from this workshop focus on inaccuracies of aneroid blood pressure measuring devices and the need to use accurate validated automated electronic monitors. This position is consistent with the HEARTS Module Access to Essential Medicines and Technology (page 37, Table 7), which indicates that validated automated electronic devices are preferred, and with the Lancet Commission on Hypertension (Sharman J et al., 2020).