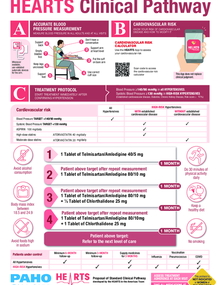
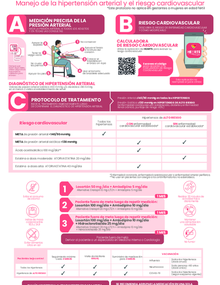
Ischemic heart disease generally refers to conditions that involve narrowing or blockage of blood vessels, caused by damage to the heart or blood vessels from atherosclerosis. A build-up of fatty plaque that thickens and hardens on the artery walls, which can inhibit blood flow through the arteries to organs and tissues and can lead to a heart attack, chest pain (angina), or stroke. Other conditions of the heart, such as those that affect the muscles, valves, or rhythm, are also considered forms of heart disease.
- More people die each year from cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) than from any other cause. Over three-quarters of heart disease and stroke-related deaths occur in low- and middle-income countries.
- The risk of CVD is increased by an unhealthy diet, characterized by a low intake of fruit and vegetables and high intakes of salt, fats, and sugars. An unhealthy diet contributes to obesity and overweight, which are also risk factors for CVD. Unhealthy eating habits can also result in a range of other conditions, including cancer, diabetes, and micronutrient deficiencies.
- People who are insufficiently active are between 20% and 30% more likely to die prematurely than those who are sufficiently active. Insufficient physical activity is a key risk factor for CVD, cancer, and diabetes.
- Tobacco use can damage every part of the body and is one of the main risk factors for CVD. It causes an estimated 10% of all CVD deaths.
Cardiovascular disease symptoms may be different for men and women and symptoms can include, chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, pain, numbness, weakness or coldness in your legs or arms if the blood vessels in those parts of your body are narrowed, pain in the neck, jaw, throat, upper abdomen or back.
Some of the risk factor for developing heart disease may include, age, sex, family history, smoking, unhealthy diet, lack of physical activity, alcohol consumption, hypertension, diabetes and obesity.
Many forms of heart disease can be prevented or treated with healthy lifestyle choices.
PAHO coordinates HEARTS in the Americas which disseminates best practices for the prevention and management of cardiovascular diseases to have a positive impact on the attributable burden of these diseases and move towards the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals 2030.
HEARTS in the Americas is an initiative of the countries, led by the Ministries of Health with the participation of local actors with the technical cooperation of PAHO, which seeks to integrate smoothly and progressively to already existing health delivery services to promote the adoption of global best practices in the prevention and control of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), and improve the performance of the services through better control of high blood pressure and the promotion of secondary prevention with emphasis on the primary health care.