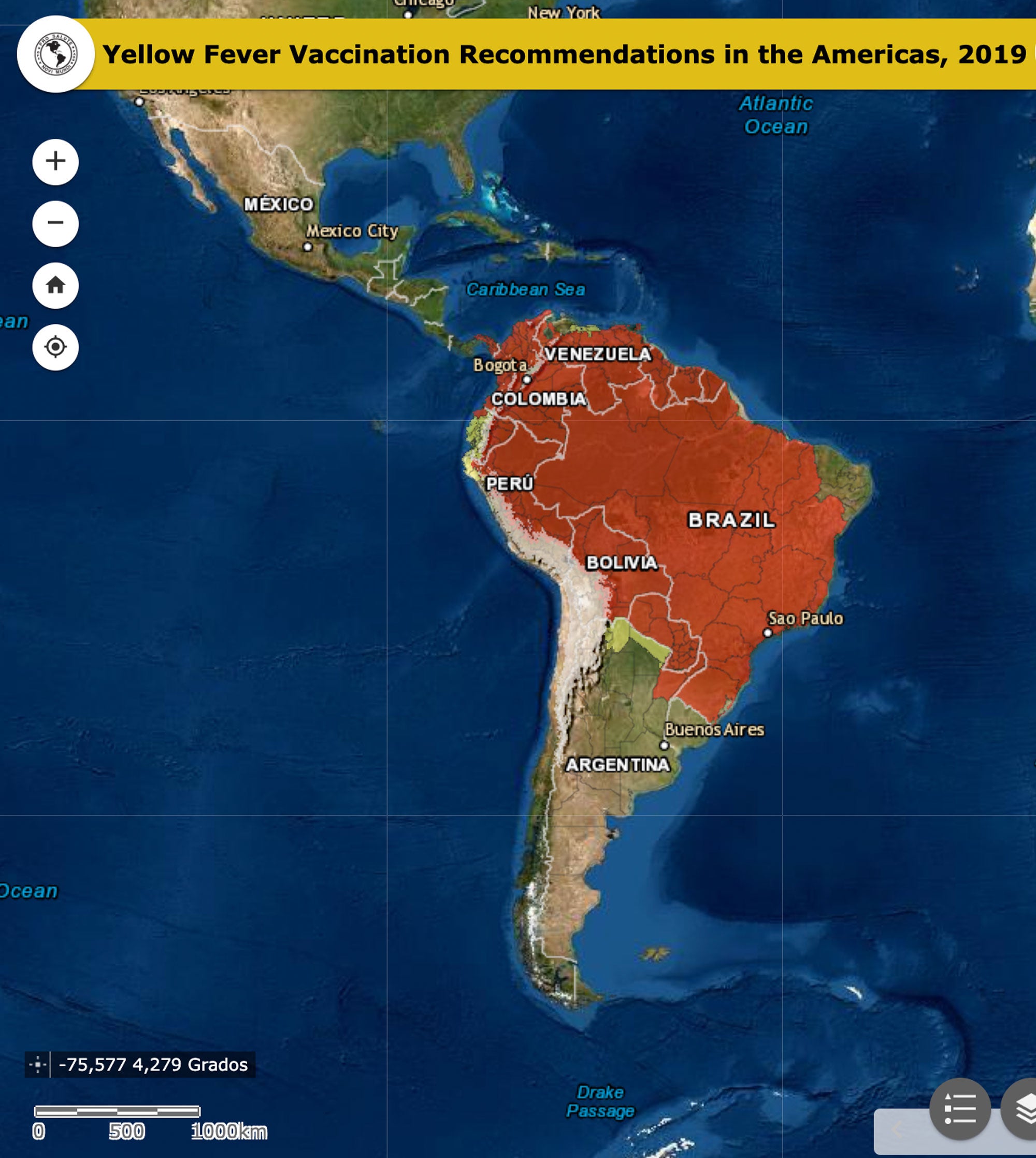
Yellow Fever Vaccine
Yellow fever is a zoonosis indigenous to some tropical regions of South America and Africa. Its etiologic agent is the yellow fever virus, an arbovirus of the genus Flavivirus (family Flaviviridae).
Transmission occurs through the bite of certain species of mosquitoes: In jungle areas of South America, by mosquitoes of the Haemagogus and Sabethes genera. In urban areas, the bite of infective Aedes aegypti mosquitoes.
Yellow fever can be prevented with live-attenuated yellow fever vaccine 17D, which is considered safe and effective, and has been used for over 60 years to actively immunize children and adults against infection with the yellow fever virus. It confers lifetime immunity.
Yellow fever vaccination strategies implemented in the Region of the Americas include:
- introduction of yellow fever vaccine into national immunization programs in all endemic countries for children aged 1 year;
- vaccination campaigns during inter-epidemic periods;
- vaccination campaigns in response to outbreaks or epizootics; and
- vaccination of travelers entering enzootic areas, except when contraindicated.
Mandates:
PAHO's (Technical Advisory Group on Vaccine-Preventable Diseases TAG) recommends that vaccination coverage for the yellow fever vaccine remains at 95% and that children must be vaccinated during their 12 months of age doctor's visit.