Promoting Food and Nutrition security for Newborns and Infants
PAHO and FIOCRUZ join efforts to reduce infant mortality in the Region through human milk banks
The Oswaldo Cruz Foundation (FIOCRUZ) is one of the most prominent health science and technology institutions in Latin America and the Caribbean. It is recognized in Brazil and other countries for its contribution to strengthening and consolidating Brazil’s Unified Health System. It also stands out as the country's main non-university institution for training and qualifying human resources.
Since its foundation in 1900, it has been dedicated to promoting health and social development, involving more than a thousand projects and programs that include research, provision of health services, production of medicines and other health technologies, training of human resources, and health information and communication, among other areas.
Collaboration between FIOCRUZ and the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) began in 1973, when the Brazilian government and PAHO signed an agreement to establish a program for developing human resources for health in Brazil. Over time, this partnership has been strengthened to include other strategic issues for public health in the country, the Region, and the world. This includes the implementation of human milk banks (HMBs), pharmaceutical assistance for the production of vaccines and medicines, South-South cooperation, and numerous other initiatives.
In view of its technical excellence, five FIOCRUZ institutes have been designated as PAHO/WHO Collaborating Centers. Among these is the Fernandes Figueira National Institute of Women’s, Children’s, and Adolescents’ Health (IFF), whose work focuses on strengthening HMBs.
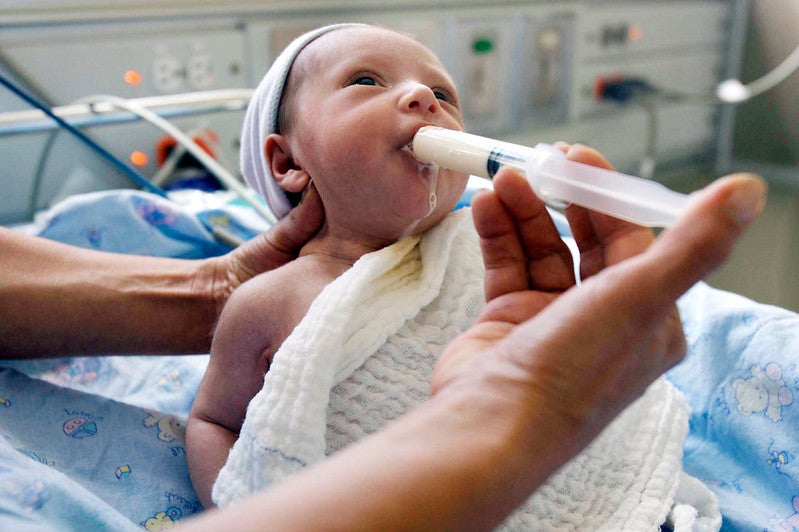
Photo credit: PAHO/Karina Zambrana
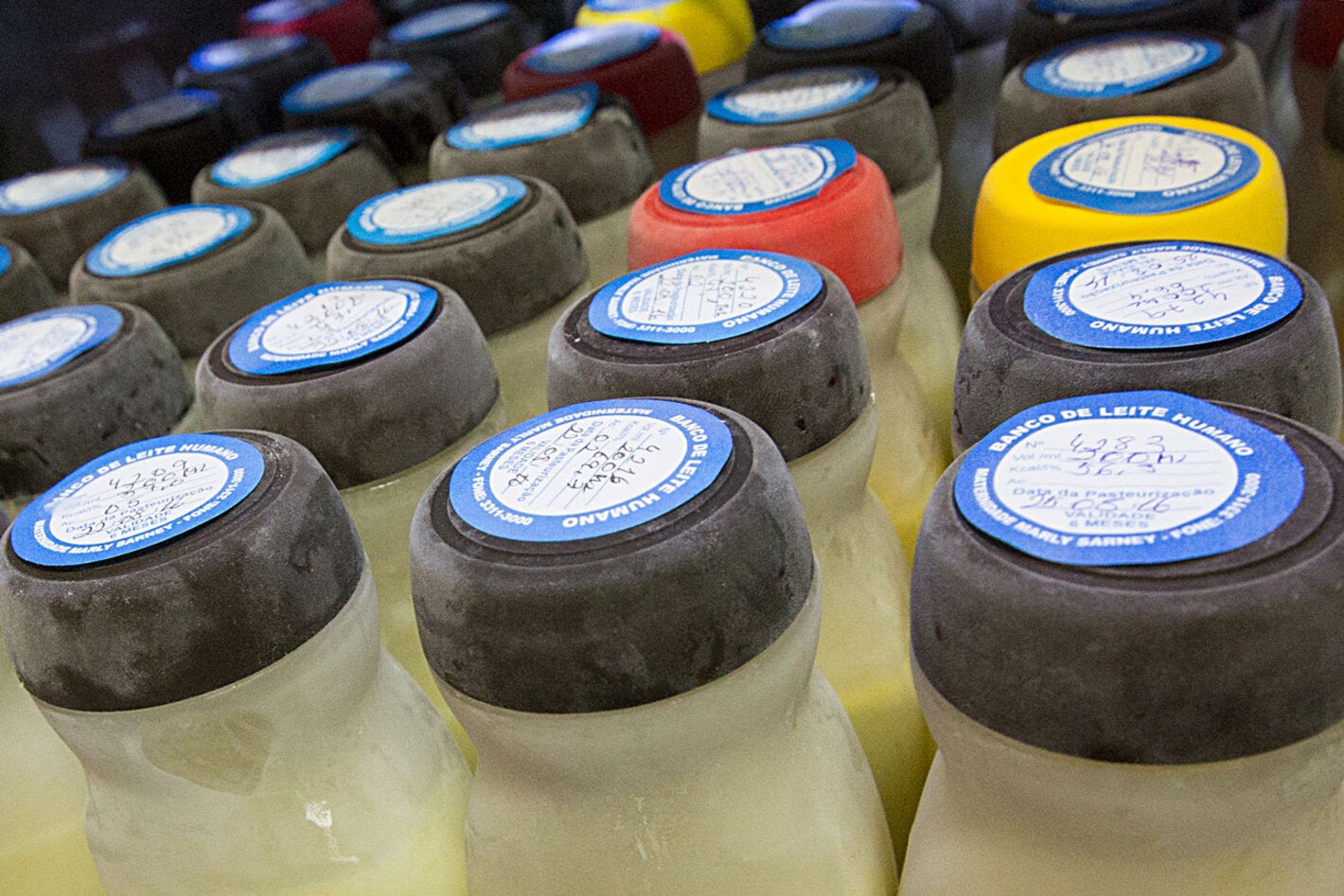
Implementation of human milk banks to promote neonatal care and protect breastfeeding
PAHO's collaboration with IFF/FIOCRUZ is technically broad and long-standing. In 2021, IFF/FIOCRUZ was designated as a PAHO/WHO Collaborating Center, and has continued to provide technical assistance to expand and share knowledge, technologies, and scientific evidence to assist its Member States in implementing and managing HMBs – a strategic action to promote neonatal care and protect the food and nutrition security of newborns and infants. In addition, through this collaboration, professional training is provided at different levels of complexity, while innovative actions are developed in the fields of research, surveillance, monitoring, and promotion of infant health.
The Brazilian model has become an inspiration to the world for its unprecedented technological development, which combines low cost with high quality, while distributing human milk based on the specific needs of each baby, thereby increasing the initiative’s effectiveness in reducing neonatal mortality. Brazil has the largest and most complex HMB network in the world, consisting of 228 operational HMBs and 236 collection stations. In addition, IFF/FIOCRUZ coordinates the Global Network of Human Milk Banks, in which 31 countries participate.
Thanks to joint work and resource mobilization, 18 countries in the Region now have milk banks. In addition to collecting, processing, and distributing human milk to premature and low birth weight babies, these HMBs provide guidance and encourage breastfeeding. Strategic collaboration with these countries has made the initiative sustainable in the participating territories.
With an extensive track record and technical excellence, IFF/FIOCRUZ is a unique PAHO partner, supporting innovative approaches and making invaluable contributions to ensuring neonatal care and reducing infant mortality. No other partner in Brazil or in the world is providing technical and strategic knowledge in this area.
With its vast experience and commitment to the countries of the Region in promoting the food and nutrition security of newborns and infants, this mission continues to expand, offering inspiration to other territories.
Additional information