Maturity Model Assessment Tools may be found in the IS4H Toolkit
The IS4H-MM is a reference framework guiding Information Systems for Health to keep walking along the path of change marked by the information and knowledge revolution, and shows how countries and organizations grow in capabilities to operate, interact and benefit from them. The diagram below illustrates the five levels of maturity
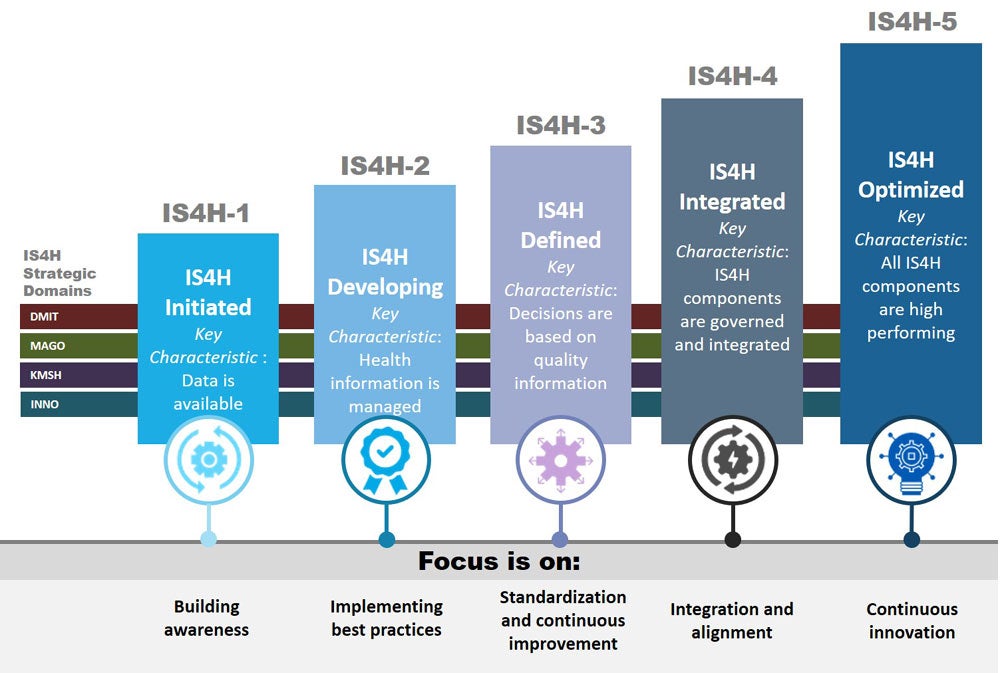
Assessment of the five progressive levels of IS4H-MM provides the awareness for planning where to go by Information Systems plans and roadmaps.
Maturity is assessed against key capability characteristics for each strategic goal at each level of the Maturity Model. It is possible for an organization to demonstrate different maturity levels within each strategic goal.
Maturity Level characteristics and components are detailed below. They are color coded according to each strategic goal of the framework that are reflected as DMIT, MAHO, KMSH and INNO in the figure above).
IS4H-MM Description
Data Management and Information Technologies (DMIT)
DMIT – Components
- Data Sources: Data collection mechanisms and technologies. Structured data refers to content that has a predefined structure and is normally classified and stored in a traditional relational database. Unstructured data refers to different types of content that that is not classified in a standard manner.
- Information Products: Health data that are processed and published openly in a variety of formats that accomplish the different needs of IS4H constituencies.
- Standards for Quality and Interoperability: Use and availability of data standards, identifiers, standards for interoperability and a national health information architecture.
- Data Governances: Health data governance is the framework for establishing sub-regional and national strategies, objectives, policies, standards, and tools for the management of technical data, which is supported by a legal framework.
- IT Infrastructure: Availability and maintenance of Tools, Networks, Hardware and Software to support IS4H. Interoperability among platforms and integration of data repositories.
DMIT – Characteristics
|
Maturity Level characteristics |
IS4H Framework Component |
|
|---|---|---|
|
LEVEL 1 |
|
Data Sources |
|
Information Products |
|
|
Standards for Quality and Interoperability |
|
|
Data Governance |
|
|
IT Infrastructure |
|
|
LEVEL 2 |
|
Data Sources |
|
Information Products |
|
|
Standards for Quality and Interoperability |
|
|
Data Governance |
|
|
IT Infrastructure |
|
|
LEVEL 3 |
|
Data Sources |
|
Information Products |
|
|
Standards for Quality and Interoperability |
|
|
Data Governance |
|
|
IT Infrastructure |
|
|
LEVEL 4 |
|
Data Sources |
|
Data Governance |
|
|
Standards for Quality and Interoperability |
|
|
Information Products |
|
|
IT Infrastructure |
|
|
LEVEL 5 |
|
Data Sources |
|
Data Governance |
|
|
Standards for Quality and Interoperability |
|
|
Information Products |
|
|
IT Infrastructure |
|
Management and Governance (MAGO)
MAGO – Components
- Leadership and Coordination: Coordination and distribution of the governance structure for IS4H accountability and decision-making at the managerial and technical level among all actors.
- Strategic and Operational Plans: Addressing IS4H under policies, strategies and SOPs at the national, regional and local level. Mechanisms for developing or adopting an IS4H governance strategy or policy that promotes a better decision- and informed policy-making mechanisms
- Organizational Structures and Functions: Organizational Structure & Information flows of health-related institutions. Roles and responsibilities IS4H health system actors.
- Financial Resources: Budget for IS4H implementation, sustainability, investment. Resources mobilization plans and ERP systems.
- Human Resources: Human capital for planning, implementing, and managing IS4H. Competency building activities to strengthen to IS4H skills. Job functions identified to effectively support IS4H.
- Multisectoral Collaboration: identification, engagement and coordination of the key actors/stakeholders for IS4H, including public–private relationship.
- Legislation, policy and compliance: Key and core legislation, policy and compliance mechanisms, elements to enable IS4H implementation, operation and maintenance.
- National and international agreements: National and International agreements to contextualize national plans and investments. Commitment to regional and global mandates.
MAGO – Characteristics
|
Maturity Level Characteristics |
IS4H Framework Component |
|
|---|---|---|
|
LEVEL 1 |
|
Leadership and Coordination |
|
Strategic and Operational Plans |
|
|
Organizational Structures and Functions |
|
|
Human Resources |
|
|
Financial Resources |
|
|
Multisectoral Collaboration |
|
|
Legislation Policy and Compliance |
|
|
National and International Agreements |
|
|
LEVEL 2 |
|
Leadership and Coordination |
|
Strategic and Operational Plans |
|
|
Organizational Structures and Functions |
|
|
Human Resources |
|
|
Financial Resources |
|
|
Multisectoral Collaboration |
|
|
Legislation Policy and Compliance |
|
|
National and International Agreements |
|
|
LEVEL 3 |
|
Leadership and Coordination |
|
Strategic and Operational Plans |
|
|
Organizational Structures and Functions |
|
|
Legislation Policy and Compliance |
|
|
Human Resources |
|
|
Financial Resources |
|
|
Multisectoral Collaboration |
|
|
National and International Agreements |
|
|
LEVEL 4 |
|
Leadership and Coordination |
|
Organizational Structures and Functions |
|
|
Human Resources |
|
|
Strategic and Operational Plans |
|
|
Financial Resources |
|
|
Multisectoral Collaboration |
|
|
National and International Agreements |
|
|
Legislation Policy and Compliance |
|
|
LEVEL 5 |
|
Leadership and Coordination |
|
Financial Resources |
|
|
Legislation Policy and Compliance |
|
|
Organizational Structures and Functions |
|
|
Human Resources |
|
|
Strategic and Operational Plans |
|
|
Multisectoral Collaboration |
|
|
National and International Agreements |
|
Knowledge Management and Sharing (KMSH)
KMSH – Components
- Knowledge Processes: Knowledge management methodologies and mechanisms to improve decision-making, capture, share and measure organizational knowledge.
- Knowledge Architecture: knowledge management and sharing policies, processes, infrastructure, tools and skills strengthening as part of a learning organization framework.
- Strategic Communications: Strategic tools and methodologies for supported decision-making. Public health communication strategy on national priority issues, as well as promoting (individual, social, and political) changes that lead to achievement and maintenance of health.
- Social Participation: Transparency and sound communication in an early stage can build trust in the system and facilitate contributions and cooperation across different sections of society. Communication and engagement with civil society and the public through mechanisms for active encouragement and transparent decision making process.
- Academia & Scientific Community: The academic and scientific communities contribute to research and producing new knowledge in health
- Networks: Different types of networks will be implemented, such as: strategic and diplomatic networks of relations, thematic and knowledge networks, and social networks for community engagement
KMSH – Characteristics
|
Maturity Level Characteristics |
IS4H Framework Component |
|
|---|---|---|
|
LEVEL 1 |
|
Knowledge Processes |
|
Knowledge Architecture |
|
|
Strategic Communications |
|
|
Social Participation |
|
|
Academia/Scientific Community |
|
|
Networks |
|
|
LEVEL 2 |
|
Knowledge Processes |
|
Knowledge Architecture |
|
|
Strategic Communications |
|
|
Social Participation |
|
|
Academia/Scientific Community |
|
|
Networks |
|
|
LEVEL 3 |
|
Knowledge Processes |
|
Knowledge Architecture |
|
|
Strategic Communications |
|
|
Social Participation |
|
|
Academia/Scientific Community |
|
|
Networks |
|
|
LEVEL 4 |
|
Knowledge Processes |
|
Knowledge Architecture |
|
|
Social Participation |
|
|
Strategic Communications |
|
|
Academia and scientific community |
|
|
Networks |
|
|
LEVEL 5 |
|
Knowledge Process |
|
Knowledge Architecture |
|
|
Strategic Communications |
|
|
Social Participation |
|
|
Academia and scientific community |
|
|
Networks |
|
Innovation (INNO)
INNO – Components
- Key concepts: Leadership and staff awareness and knowledge of IS4H key concepts:
- Big data
- Open Data
- Predictive analytics
- Social analytics
- Forecasting
- Modelling
- And more…
- Health Analysis for Decision-Making: A systematic approach for health needs assessments; accessibility of essential information; advanced analytical techniques to support real time clinical, management, policy and decision making.
- Tools: Health analysis and business intelligence tools are available for advanced approaches to health information.
- Digital Health: Digital health tools being used to transform models of care, improve patient safety, quality of care and supporting population health approaches. Health care and service are delivered virtually.
- E-Government: Integration of the health sector on the eGovernment initiatives, including the adoption of standards, applications, and information services to transform transactions between government and the public, businesses, or other organizations in health.
- Open Government: Public access and effective oversight to government documents and proceedings. Open Data principles application and data sets availability.
- Preparedness and Resilience: Capacity of the information systems for health to operate during and after emergencies and disasters requires the development and application of special operating procedures to ensure access to the right information at the right moment in the right format.
INNO – Characteristics
|
Maturity Level Characteristics |
IS4H Framework Component |
|
|
LEVEL 1 |
|
Key Concepts |
|
Health Analysis for Decision-making |
|
|
Tools |
|
|
Digital Health |
|
|
eGovernment |
|
|
Open Government |
|
|
Preparedness and Resilience |
|
|
LEVEL 2 |
|
Key Concepts |
|
Tools |
|
|
Health Analysis for Decision-making |
|
|
Digital Health |
|
|
eGovernment |
|
|
Open Government |
|
|
Preparedness and Reliance |
|
|
LEVEL 3 |
|
Key Concepts |
|
Health Analysis for Decision-making |
|
|
Tools |
|
|
Digital Health |
|
|
eGovernment |
|
|
Open Government |
|
|
Preparedness and Resilience |
|
|
LEVEL 4 |
|
Health Analysis for Decision-making |
|
Tools |
|
|
Key Concepts |
|
|
Digital Health |
|
|
Open Government |
|
|
Preparedness and Resilience |
|
|
eGovernment |
|
|
LEVEL 5 |
|
Health Analysis for Decision-making |
|
Tools |
|
|
Key Concepts |
|
|
Open Government |
|
|
Preparedness and Resilience |
|
|
eGovernment |
|
|
Digital Health |
|
