SIMPLE TREATMENT PROTOCOLS
An effective strategy for rapid improvement in hypertension control rates is to implement a population-based, standardized antihypertensive pharmacologic treatment protocol, and securing the availability and affordability of high-quality antihypertensive medications.
Patients benefit when clinics expand the number of health workers who can provide, adjust and intensify medication regimens per physician orders and protocols. It is critical to get the right medications to the right place at the right time to reach the patients who need them. Regular and uninterrupted medications are necessary for treatment.
Patient-centered care can reduce barriers to controlling blood pressure. Strategies include easy-to-take medicine regimens, free or low-cost medications and follow up visits, and readily available blood pressure monitoring.
Hypertension Clinical Pathway
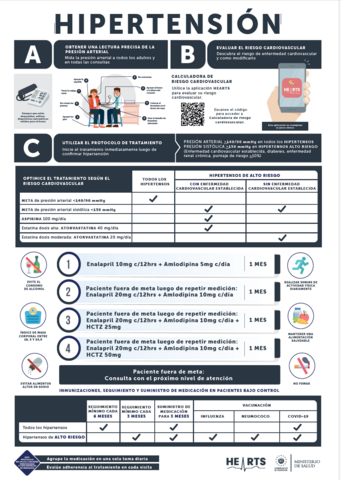
HEARTS in America has developed the Hypertension Clinical Pathway aiming to catalyze the implementation of the new 2021 WHO hypertension guideline recommendations and the hypertension control drivers. This tool will help countries implementing HEARTS define their standardized treatment protocols, integrate relevant components of proper blood pressure measurement, assess cardiovascular risk and patient care based on their risk, and strengthen the integration of diabetes and chronic kidney disease for cardiovascular prevention at primary health care.
1. AMLODIPINE (5 mg)
2. CHLORTHALIDONE (12.5 mg; 25 mg)
3. LISINOPRIL (20 mg; 40 mg)
4. LISINOPRIL + AMLODIPINE (10 mg + 5 mg; 20 mg + 5 mg; 20 mg + 10 mg)
5. LISINOPRIL + HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE (10 mg + 12.5 mg; 20 mg + 12.5 mg; 20 mg + 25 mg)
6. TELMISARTAN (40 mg; 80 mg)
7. TELMISARTAN + AMLODIPINE (40 mg + 5 mg; 80 mg + 5 mg; 80 mg + 10 mg)
8. TELMISARTAN + HYDROCHLOROTHIAZIDE (40 mg + 12.5 mg; 80 mg + 12.5 mg; 80 mg + 25 mg)